When we talk about big data, most people think of huge, complicated datasets and the challenges of managing them. For many companies, this exponential data growth from applications, IoT, and analytics is a double-edged sword. How can one store, process, and analyze petabytes of data quickly and affordably?
Azure Data Lake Storage is Microsoft's solution to this big data dilemma. Out of all the cloud service providers, it is the most advanced and most cost-effective. If your company is looking for a data repository where all data can be housed and analyzed, this is the article for you. By the end of this article, you will ascertain how ADLS can be utilized to support the analytics and AI goals of your company.
What Is Azure Data Lake Storage?

Azure Data Lake Storage is a highly scalable and secure cloud storage service designed specifically for big data analytics workloads. It is like a centralized unit that gathers and retains all data values in raw character and native format, regardless of their structure, for future processing.
More technically, ADLS Gen2 is the most recent version and is developed over Azure Blob Storage. It combines the tiered cloud low-cost storage and the enhancements added for big data with hierarchical namespace and granular security to enable complex, advanced, and analytical data queries.
Further, ADLS is capable of storing and analyzing petabytes of data while maintaining a consistent throughput of hundreds of gigabits, making it preferable for companies wanting big data machine learning and real-time analytics processing.
Unlike other cloud storage options, Azure Data Lake Storage provides the following benefits:
Analytics Optimization: Purpose-built for high-performance analytics engines.
Hierarchical Structure: Organizes files in a directory structure, just like a local file system, which is crucial for big data frameworks.
Massive Scalability: No limits on account size, file size, or the amount of data stored.
Why Do Companies Need a Data Lake?
Companies capture a variety of data from multiple sources these days. From social media posts to capture customer sentiment, to IoT sensors to interpret customer behavior, to data on customer transactions, the variety of data sources available is endless. Typical data warehouses are unable to accommodate such a variety of sources, as they require data to have a pre-defined structure.
This is the gap a data lake fills. They offer a single location where data can be stored in any format. They allow the preservation of raw data, which is invaluable for future raw data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. You do not have to be tied to a rigid storage structure.
Here’s a quick comparison of data lakes and data warehouses:
Feature | Data Lake | Data Warehouse |
Data Structure | Raw, unstructured, semi-structured, structured | Structured, processed |
Schema | Schema-on-read (defined during analysis) | Schema-on-write (defined before storage) |
Primary Users | Data scientists, data engineers, analysts | Business analysts |
Use Cases | Machine learning, predictive analytics, data exploration | Business intelligence (BI), reporting |
Flexibility | High | Low |
Azure Data Lake Storage vs. Azure Blob Storage
Azure Data Lake Storage and Azure Blob Storage can sometimes be used interchangeably, as Blob Storage is Azure's foundation for both services. However, they each have their own specific use cases.
Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS Gen2) is optimized for big data analytics use cases. One of the benefits of ADLS Gen2 is that it implements a hierarchical namespace, which allows users of the analytics service to structure their data and folders the same way they do in their local file system. This is well-suited for analytics workloads that require frequent reads and writes to the storage at specific data folders.
Azure Blob Storage is a general object storage solution, and is a good fit for use cases such as storing unstructured data, including images, videos, and documents, as well as data backups and backups of unstructured data. Blob Storage uses a flat namespace architecture, with all objects inside a container being at the same nesting level.
When should you use each?
Use Azure Data Lake Storage for:
Analytics processing on a large scale, which can be done using Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, or HDInsight.
Building machine learning pipelines that require large-scale data processing.
IoT data ingestion and real-time processing.
Use Azure Blob Storage for:
Backup and archival file storage, as well as disaster recovery.
Directly streaming video and audio content to the user.
Embedding content such as documents or images directly in the browser.
Think of it this way: if you just need a place to park your files, Blob Storage is the perfect choice. If, on the other hand, you wish to run advanced high-performance analytics on those files, then your best option is Azure Data Lake Storage.
Key Features of Azure Data Lake Storage
ADLS comes packed with features designed to meet the requirements of enterprise storage and big data analytics:
Unlimited Scalability: Store and analyze petabytes of data with total peace of mind. The system scales automatically to meet your needs.
Native Integration: It integrates smoothly in the entire Azure Ecosystem, Azure Databricks, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Power BI, and allows the creation of complete analytics and ASPs (Application Service Provider) in Azure.
Hierarchical Namespace: Hierarchical Namespace is the one that analytics performance benefits the most from. HNS allows the system to quickly and efficiently perform operations such as renaming, moving, or deleting large sets of directories in a structure. This is a behavior that is analogous to the behavior of the Hadoop distribution file structure, and especially compatible with all tools available for big data.
Enterprise Security & Compliance: ADLS comprises a full spectrum of enterprise-grade security features, and support with Microsoft Entra ID integration for role-based access control imposition, a layer of POSIX-like access control lists for more granular control, data encryption at rest and in transit, and network security for protective offsets and firewalls.
Multi-Protocol Access: With ADLS, you can use either the Data Lake Storage Gen2 API or the Blob Storage API to access your data. This allows you to use multiple tools and applications without having to move or duplicate your data.
Azure Data Lake Pricing: How It Works
Understanding Azure Data Lake pricing is important for cost management. The model is built on several components, so the details are below:
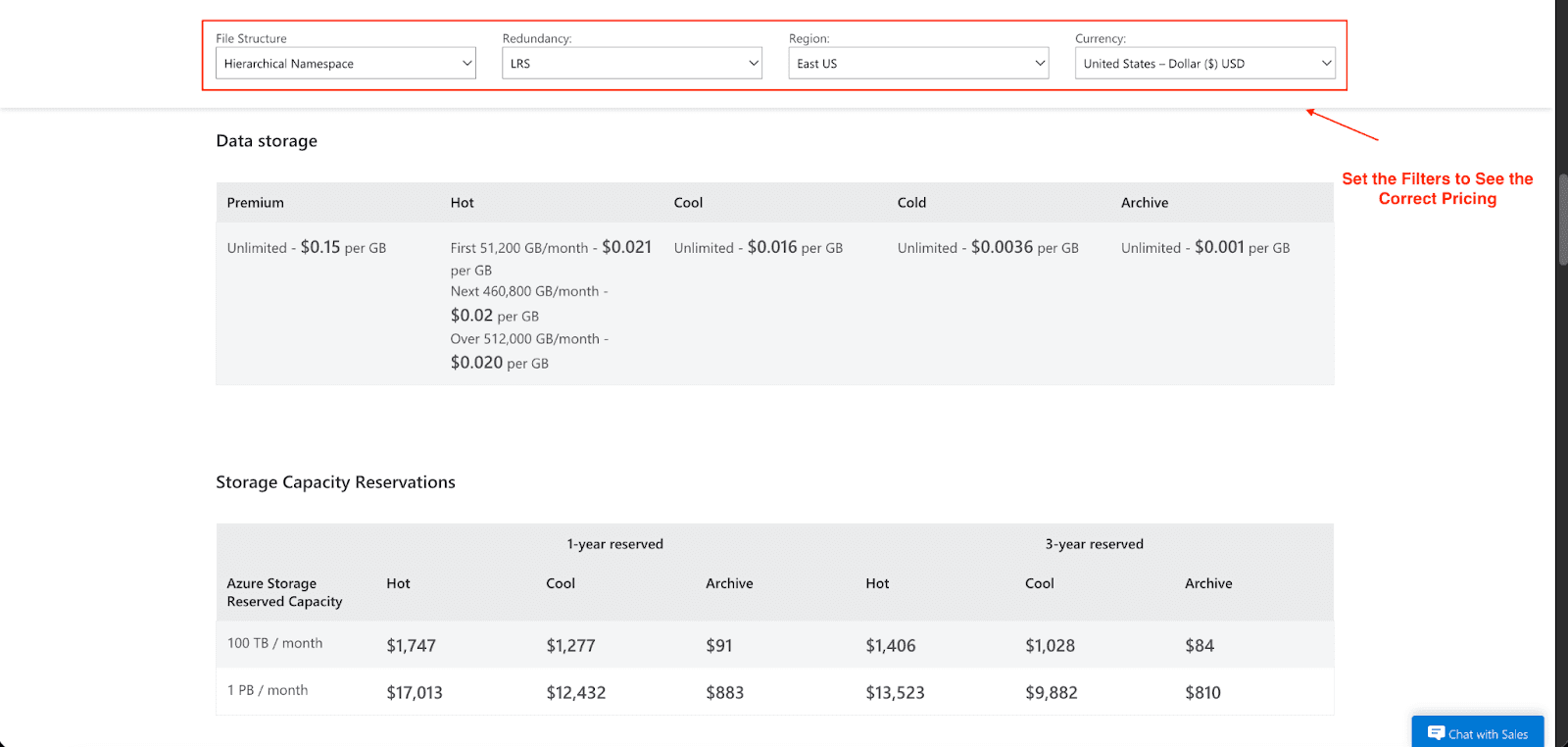
Storage Costs: You pay monthly for the amount of data you store as well as the storage tier, which could be Premium, Hot, Cool, Cold, or Archive. There are also multiple redundancy options available to choose from, which include: LRS, GRS, and ZRS. An example of this is that while the Premium tier charges $0.15 for every GB of data, the hot tier charges $0.021 for the first 50 TB per month. The costs can be reduced to a great extent by buying a reserved capacity, which could be for one or three years at a time. Therefore, for 100 TB reserved for 3 years, at the Hot tier, the price would be $1,406, whereas the price for one year is $1,747.
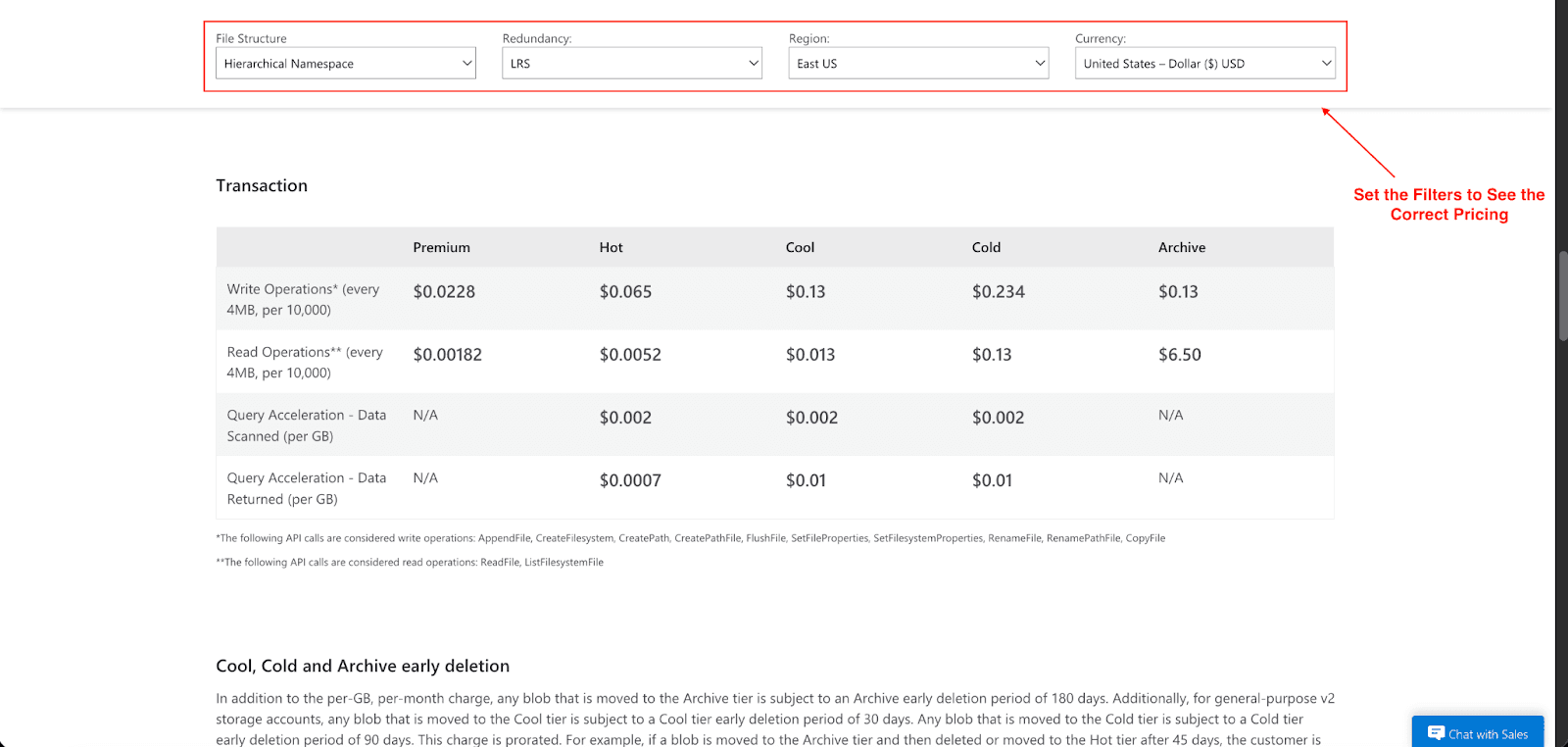
Transactions and Data Access Operations: You're charged for actions like reading, writing, and listing data. Each operation is billed at a rate of per 10,000 and can depend on the type of operation and what tier the storage is in. For example, in the Hot tier, a write operation costs $0.065 for every 10,000 write requests, and a read operation costs $0.0052 per 10,000 requests. A lot of small files tend to be expensive due to the operational costs and interaction, so the best practice to limit costs is to consolidate your data into bigger files. Data in the range of 256 MB to 100 GB is a good range as it doesn't incur high costs. As there is an operational cost to every interaction, small files should be avoided.
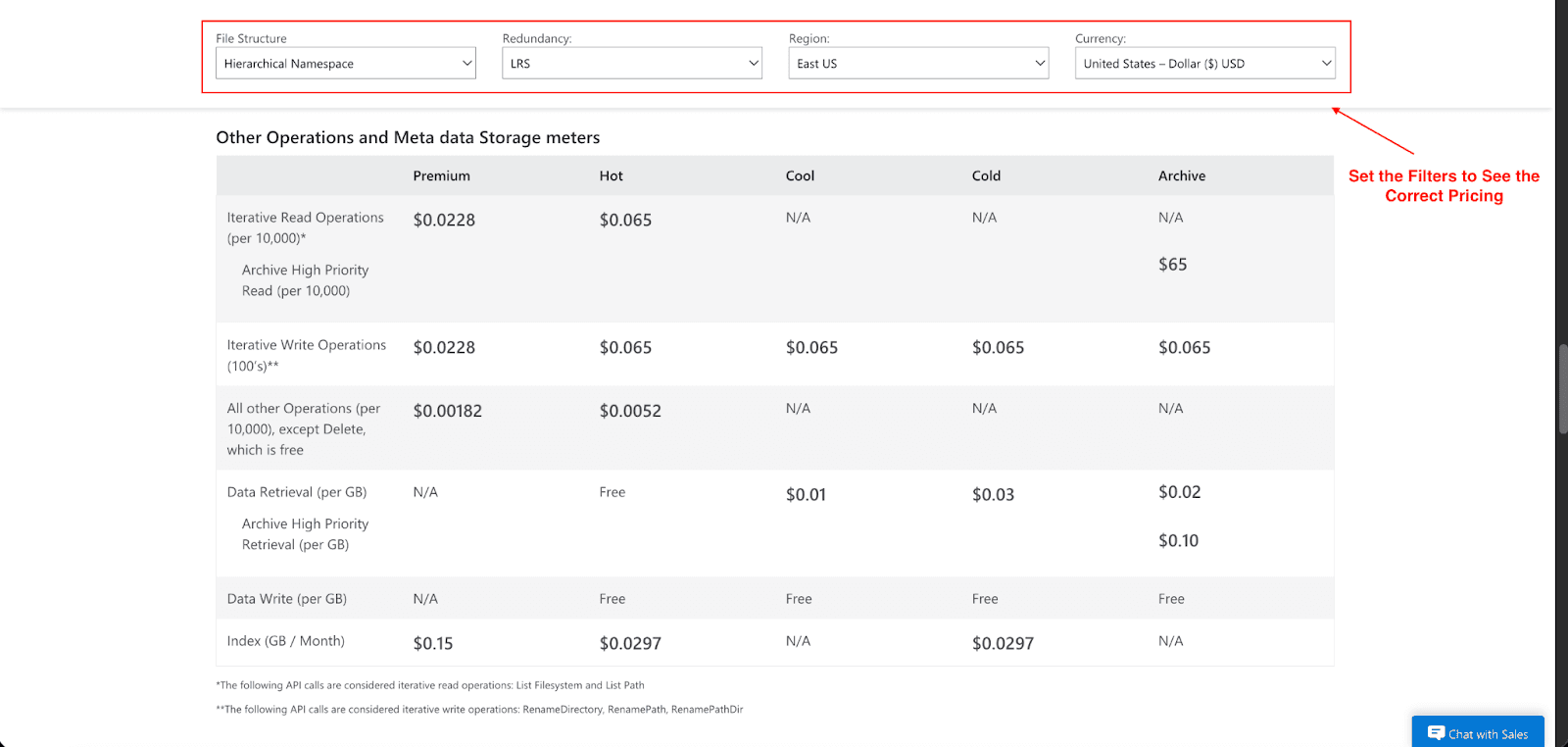
Data Retrieval Costs: This is the cost to access your data. Think of it like a valet service for your files. With the various tiers where data is being stored, there can be a per-GB fee to you when it's brought to you as the valet service offered. For example, data retrieval costs for the Cool tier are $0.01 per GB, and for the Cold tier, it's $0.03 per GB. There are no retrieval costs when the data is in the Hot tier and is always set to be in that tier, as it is always ready for immediate access.
Network Egress Fees: Think of this as a shipping fee for your data. Every time you move data from one Azure region to another zone, you’re charged for the use of the network bandwidth. These costs are not the same as the costs of storage or transactions. If enormous data sets are transferred regularly, these costs accumulate rapidly.
Hidden costs to watch for:
Query Charges: As far as ADLS is concerned, there is no charge for queries; however, analytics services that run on top, such as Azure Synapse or Databricks, have their own pricing models.
Data Movement: Moving data into ADLS and out of ADLS and into another service will incur data transfer and/or bandwidth costs.
Hierarchical Namespace Costs: When the Hierarchical Namespace feature is set, creating a file system-like structure with folders and directories actually does not raise your per-GB storage cost, but rather initiates charges associated with the metadata and directory administrative overheads. More often than not, these dues are more likely than not to be overlooked as they are grouped in the bill, but they do land as a separate line of transactions/operations fees.
To estimate your costs, you can use the Azure pricing calculator. Prior to scaling up the deployment, do a small trial run to help evaluate what the services will actually be doing, with careful consideration to service utilization. It is also good practice to open a free subscription first.
Best Use Cases for Azure Data Lake
Azure Data Lake is a versatile solution that supports a wide range of applications across various industries:
Machine Learning: You can save and pre-process large volumes of data to train your ML models and build them at scale using Azure Machine Learning's seamless integration to deploy your models.
IoT Pipelines: Stream data in real-time from your IoT devices to store and analyze. The capability to organize data hierarchically (i.e.,/yyyy/mm/dd/hh/) enhances query performance on time series data.
BI and Reporting: Act as a single source of truth for BI platforms like Power BI - analysts can use the data lake to connect and curate interactive dashboards and reports.
Enterprise Archives: Retain data for extended periods at low cost to meet data governance requirements while also complying with retention policies using the Archive tier.
When Is Azure Data Lake Storage Not the Best Option?
However, there are some scenarios where the Azure Data Lake isn't the right option:
Low-Latency Transactional Systems: For applications that require lower and more consistent latency and higher IOPS, say, the backend of an e-commerce site, a relational or NoSQL database would fit better.
Simple Object Storage: If the workload does not involve any analytics, Azure Blob storage is much simpler to manage and more cost-effective.
Preference for Other Ecosystems: If your enterprise is heavily invested in other cloud ecosystems, alternatives such as Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage may integrate better with the rest of your toolkit.
Conclusion
Azure Data Lake Storage is a robust, scalable, and secure option for the management of extensive data sets and supports advanced analytics and AI initiatives. Consolidating data allows teams to draw insights and propel innovation. For both novices in big data or those with a more advanced setup, Azure Data Lake Storage is the right option.
I hope you’ve learned everything about Azure Data Lake features, pricing, and optimization savings tips. Ready to explore its potential? Start with an Azure free trial today.
Join Pump for Free
If you are an early-stage startup that wants to save on cloud costs, use this opportunity. If you are a start-up business owner who wants to cut down the cost of using the cloud, then this is your chance. Pump helps you save up to 60% in cloud costs, and the best thing about it is that it is absolutely free!
Pump provides personalized solutions that allow you to effectively manage and optimize your Azure, GCP, and AWS spending. Take complete control over your cloud expenses and ensure that you get the most from what you have invested. Who would pay more when we can save better?
Are you ready to take control of your cloud expenses?




