
When I think about how companies store and analyze data today, cloud data warehouses immediately come to mind. Having spent a good chunk of time building data ecosystems, I can’t ignore the two names that keep appearing: Amazon Redshift and Snowflake. Both deliver impressive performance at petabyte scale, yet the architectural, pricing, and management paths they follow could hardly look more different.
In this comparison, I’ll walk you through the most important differences. At the end, I’ll provide some practical criteria that may help you choose the platform best suited to your company, not just for today, but for how you envision evolving data workloads.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse serves as a centralized vault for massive volumes of structured and semi-structured data consolidated from disparate sources. Unlike operational databases, which optimize transactional workloads, warehouses are purpose-built to answer analytical questions quickly, to feed dashboards and predictive models.
Modern cloud data warehouses offer several advantages over traditional on-premises solutions:
Limitless scale that adjusts to load.
Pay-as-you-use pricing models.
Much less time spent on managing and patching physical infrastructure.
Built-in security and compliance features.
Thanks to these characteristics, companies of any scale can now apply advanced analytics, creating broader and deeper insights from business data that would otherwise remain stranded in siloed systems.
Why Compare Redshift and Snowflake?
Choosing between Redshift and Snowflake is more than a technical decision; it’s a question of aligning with a data warehousing philosophy that matches your long-term strategy. Redshift ties itself into the AWS family with rich integration tools and a familiar operational model, whereas Snowflake promises portability across clouds and a separation of storage and compute that changes the way you think about scaling. Developer teams and analysts will be living with the consequences of either model for years, so grasping these contrasting principles will help you stay on point with costs, compliance, and performance.
What is AWS Redshift?
Amazon Redshift is a petabyte-scale, fully managed data warehouse that builds on AWS’s robust global infrastructure. Since its initial release in 2013, it has drawn organizations that have already staked their cloud strategy on AWS services. By employing a columnar storage format alongside a Massively Parallel Processing architecture, Redshift accelerates analytic workloads across massive tables. The architecture is centred on a leader node that compiles and orchestrates queries and multiple compute nodes that handle the legwork in parallel, balancing speed with the cloud-scale elasticity AWS is known for.
Key Features and Benefits
Redshift remains a compelling choice for enterprise-scale analytics for the following reasons:
Native AWS Integration: Out-of-the-box connectivity to AWS components such as S3 for storage, Glue for ETL processes, and Kinesis for real-time data streams.
Advanced Query Optimization: The engine applies automatic tuning and uses result caching to accelerate frequently run analyses.
Flexible Node Types: Companies can select from compute-optimized or storage-optimized nodes to align performance with workload patterns.
Machine Learning Integration: Native machine learning functionality via Redshift ML, enabling in-database model building
Comprehensive Security: Encryption both at rest and in flight, full VPC support, and seamless integration with AWS Identity and Access Management
What is Snowflake Data Warehouse?

Snowflake is a fully cloud-native data platform designed exclusively for elastic cloud environments. Unlike traditional solutions, it decouples compute and storage workloads, letting organizations independently and instantaneously scale resources to match workload demands without sacrificing performance.
Snowflake delivers data warehousing functionality as a managed Software-as-a-Service offering, transparently running on top of AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP resources. By adopting a multi-cloud architecture, organizations avoid vendor lock-in while ensuring data residency and low-latency access for globally distributed teams.
Key Features and Benefits
Key characteristics that differentiate Snowflake include:
Automatic Scaling: Scale compute resources in seconds, scale storage instantly, all without stopping the business.
Zero-Copy Cloning: Duplicate entire datasets in a fraction of a second without moving or re-storing the underlying data.
Time Travel: Retrieve and analyze data exactly as it appeared one week or one month ago, in a single historical snapshot.
Data Sharing: Grant external partners or departments real-time access to a view of data, with fine-grained security and no data movement.
Multi-Cloud Support: Flexibly operate workloads on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, optimizing for regional latency.
Redshift vs Snowflake: Head-to-Head Comparison
Feature | Snowflake | Amazon Redshift |
Architecture | Multi-cluster, shared data, decoupled compute/storage | Clustered nodes, coupled compute/storage |
Cloud Providers | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud | AWS only |
Scaling | Instant automatic scaling, independent compute/storage | Manual scaling, resize takes 15-60 minutes |
Data Types | Structured + comprehensive semi-structured support | Structured + limited semi-structured JSON |
Performance | Consistent with workload isolation | Flat cost but performance degrades under load |
Management | Fully managed, automated optimizations | More hands-on, requires tuning |
Pricing | Separate compute and storage billing | Bundled compute and storage billing |
Security | Role-based access control, encryption varies by tier | AWS IAM integration, flexible encryption |
Availability | Multi-region, cross-cloud replication | Multi-AZ deployments, cross-region snapshots |
Advanced Features | Time travel, zero-copy cloning, Snowpark, automatic clustering | Spectrum for querying S3, federated queries, auto table optimization |
Pricing and Value Comparison
Redshift vs Snowflake pricing comparison highlights contrasting models for workload budgeting:
Redshift Pricing:
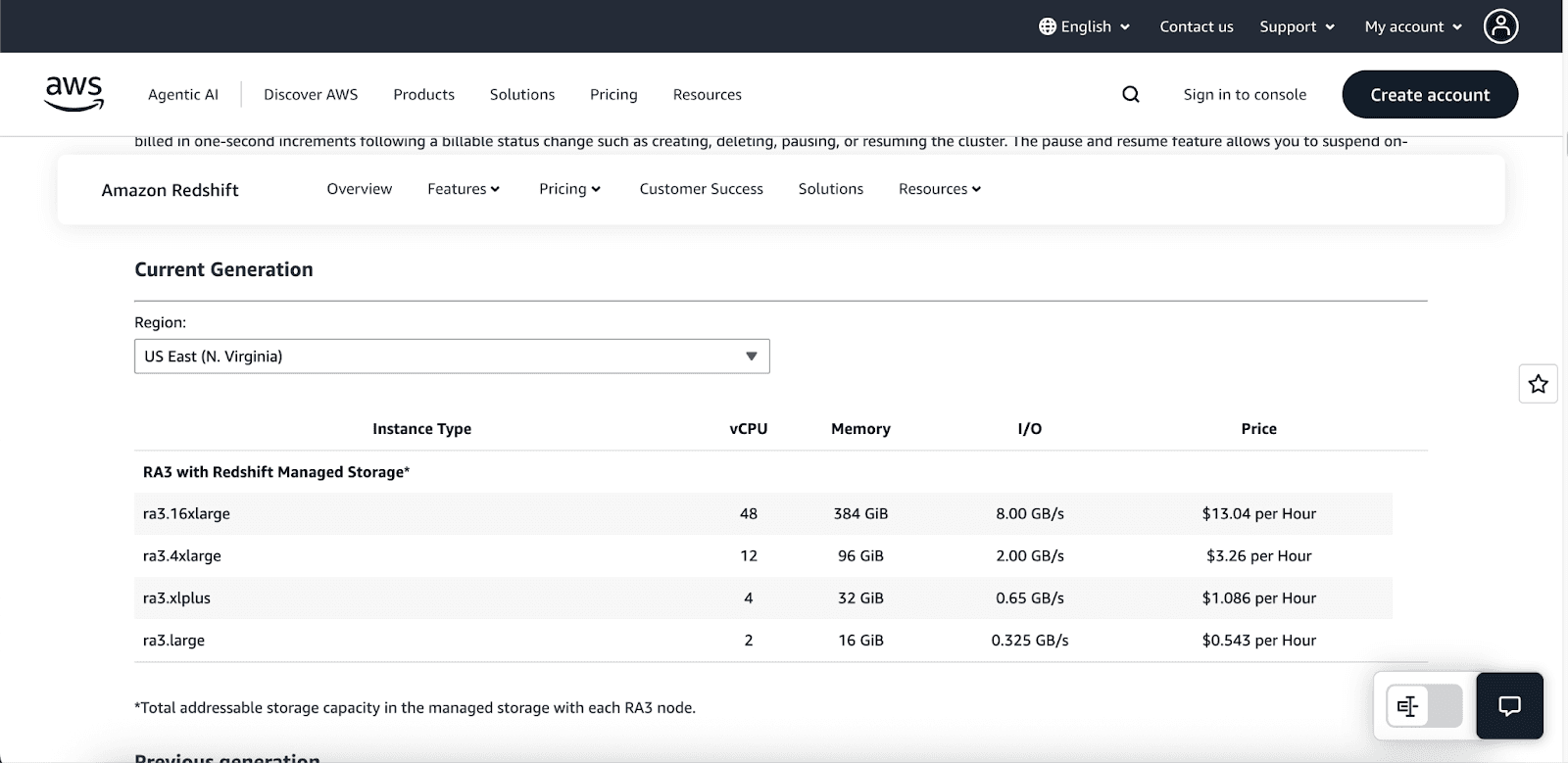
On-Demand: Starts at approximately $0.543 per hour with no commitments; pricing varies by node type (e.g., DC2.large ~$0.33/hour, DC2.8xlarge ~$6.40/hour).
Reserved Instances: 1- or 3-year commitments for up to ~75% savings.
Serverless: Starts at $1.50/hour, with billing based on Redshift Processing Units (RPUs) metered per second (minimum 60 seconds). Some estimates suggest usage can start around $3/hour (RPUs priced at ~$0.375 per RPU-hour).
Storage Costs: Managed Storage (RA3 nodes) costs around $0.024 per GB-month.
Redshift Spectrum: Queries over S3 cost approximately $5 per TB scanned.
Additional Features: Includes 1 free hour of concurrency scaling credits per 24 hours, with separate costs for snapshots and data transfers.
Snowflake pricing:
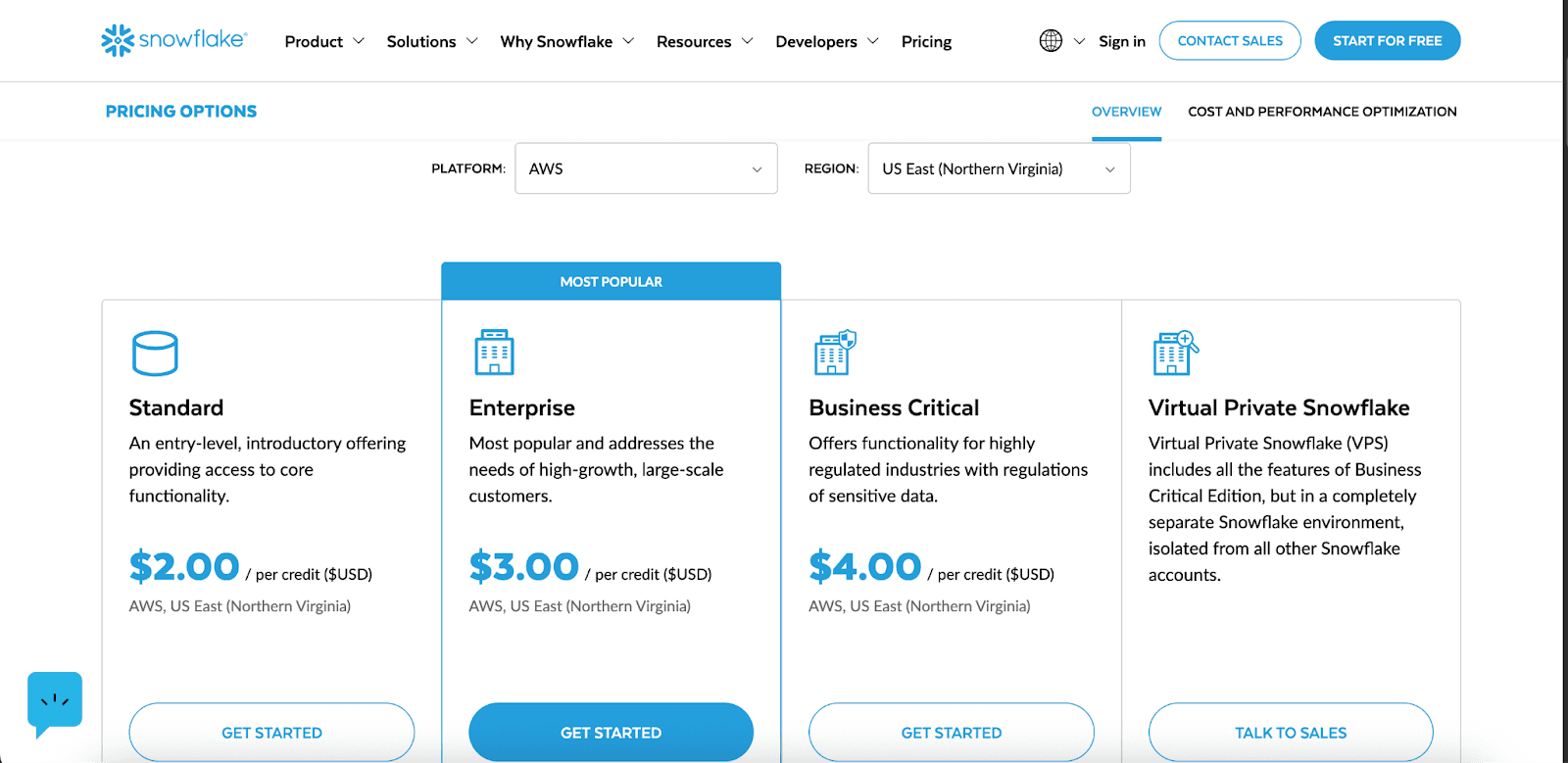
Compute (Virtual Warehouses): Virtual warehouses are billed based on credits per hour. Costs start at 1 credit/hour for X-Small warehouses, increasing to 8 credits/hour for Large warehouses, and up to 512 credits/hour for 6X-Large. Snowpark-optimized variants require 1.5× or more credits (e.g., Medium warehouses are 6 credits/hour). Billing is per second, with a 60-second minimum.
Storage: Compressed data storage costs around $23 per TB per month in US regions, with lower rates for pre-purchased capacity. Features like Time Travel and Fail-safe incur additional charges. Storage is billed separately from compute.
Data Transfer & Services: Ingress (data imported into Snowflake) and same-region transfers are free. Cross-region and cross-cloud egress charges vary based on the region. The cloud services layer (e.g., metadata services) is included, provided usage doesn’t exceed approximately 10% of warehouse compute usage.
Maintenance & Automation
Snowflake Automation removes day-to-day tasks by delivering a managed model with no admin requirements.
Performance enhancements happen automatically; there’s no tuning to schedule.
Clusters, storage, and micro-partitioning adjust on their own.
Compute and storage scale independently, in the background and without fuss.
Functions like auto-suspend and auto-resume match activity with cost efficiency in real time.
With Amazon Redshift, hands-on oversight includes deliberate tuning, such as:
Configuring distribution and sort keys to shape queries and balance data.
Carrying out VACUUM and ANALYZE to reclaim space and refresh statistics.
Adjusting Workload Management for better concurrency.
Resizing clusters manually and overseeing node changes, often with a risk of downtime.
Special Features & Use Cases
Serverless & Multi-Cloud
Redshift Serverless automatically provisions compute resources and scales them dynamically based on real-time workload patterns, charging only for capacity consumed. This capability alleviates the burden of cluster management yet remains anchored within the AWS universe.
Snowflake delivers genuine multi-cloud support, permitting workloads to run on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. Its built-in cross-cloud replication and sharing features create a seamless environment for data that must travel or collaborate beyond a single cloud. Such architecture bolsters multi-cloud initiatives by minimizing vendor lock-in while retaining easy cross-cloud access.
Semi-Structured Data & Machine Learning
Redshift enriches its semi-structured data capabilities via the SUPER data type, allowing direct JSON ingestion. The platform processes nested structures flexibly through native PartiQL queries, streamlining the analysis of hierarchical data without intermediate extraction.
Redshift ML empowers users to build, train, and operationalize machine learning models solely through SQL. The feature works hand-in-hand with Amazon SageMaker, enabling model lifecycles within the same compute context as the data.
Snowflake adds a contrasting approach with Snowpark, a developer framework permitting Java, Scala, and Python to run natively on Snowflake. This model enables sophisticated data science and machine learning activities within the platform itself, eliminating the need for data export while ensuring consistent execution environments.
Advanced Features
Snowflake’s Time Travel capability provides access to data as it existed at any point within a user-defined retention window (1 day by default, extendable to 90 days in Enterprise), simplifying processes like recovery, compliance auditing, and forensic analysis.
Snowflake’s Data Sharing feature promotes secure, real-time collaboration between different organizations without the need to copy or transfer data, paving the way for data monetization and the establishment of interconnected ecosystems.
Cut Cloud Costs with Pump
If you are looking to reduce costs on your Redshift, we will help you to reduce costs. For example, if your incentive bill is at $100, using Pump can bring it down to $44. This tool is particularly useful as your costs tend to be on the higher end because it saves more when the costs are higher. But while we are at it, why not think about the features we intend to release for Snowflake down the road. Right now the focus is on cost savings for Redshift and other AWS and GCP Services.
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Your Needs?
In the Redshift vs Snowflake comparison, the goal is matching the platform to your environment rather than seeking a universally superior choice:
Choose Amazon Redshift if you:
Leverage considerable AWS infrastructure.
Operate predictable, steady workloads.
Want aggressive savings via elapsed-usage Reserved Instances.
Require deep AWS service integration.
Choose Snowflake if you:
Face variable or unpredictable workloads.
Require immediate, nondisruptive scaling.
Desire minimal ongoing operational management efforts.
Require multi-cloud deployment flexibility.
Both platforms are strong contenders for contemporary data warehousing. An optimal choice rests on a thorough analysis of precise use cases, current architecture, and intended data governance path.




