Enterprise databases have evolved from simply being a repository of stored information. As someone who has witnessed the ever-changing needs of a company, I understand that companies have started demanding intelligent, scalable solutions that handle intricate workloads whilst still being compatible with aged systems like PostgreSQL. This is right where Google Cloud's AlloyDB for PostgreSQL shines, an ever-managed database solution which combines PostgreSQL's reliability with AI-powered features and cloud-driven performance.
In this article, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about AlloyDB, from the most prominent features to the pricing model. I trust this serves as valuable information for, be it a start-up weighing their options or an enterprise preparing for a migration, as you develop data infrastructure. Let’s get started.
What is GCP AlloyDB?

AlloyDB is an innovative addition to Google Cloud intended to fit the most challenging workloads in Postgres. It is an AlloyDB for Postgres system, which is also a fully managed system. It functions differently from a traditional Postgres system in that AlloyDB’s compute layer is disaggregated from its storage layer, allowing for segregated workloads to function without impact on performance.
AlloyDB also possesses a 100% open-source Postgres coverage, containing all the same extensions, which allows for a seamless migration for previous workloads to Postgres, thus benefiting from enhanced performance, AI systems, and reliability.
AlloyDB’s integration into the Google Cloud is seamless, especially in comparison to:
Cloud SQL: Simpler, managed relational database for standard workloads.
AlloyDB: Best of both worlds: relational + analytical capabilities with PostgreSQL familiarity.
Spanner: Globally distributed, strong-consistency relational database.
BigQuery: Data warehouse for large-scale analytics.
Firestore: NoSQL, document-based database for real-time apps.
Due to the excellent performance in transactional and analytical workloads, the service is perfect for use cases that require real-time analytics and flexible operations.
Key Features of GCP AlloyDB
PostgreSQL Compatibility
AlloyDB maintains complete openness to PostgreSQL’s databases via direct protocol, along with supporting convenient extensions to queries and syntax. Doing so mitigates vendor lock and allows developers to take advantage of readily available PostgreSQL skill sets and tools.
The compatibility includes PostGIS for geospatial data, pgvector for vector operations, and other popular custom application extensions. Migration from current PostgreSQL instances is equally simple, requiring no code changes.
High Performance & Scalability
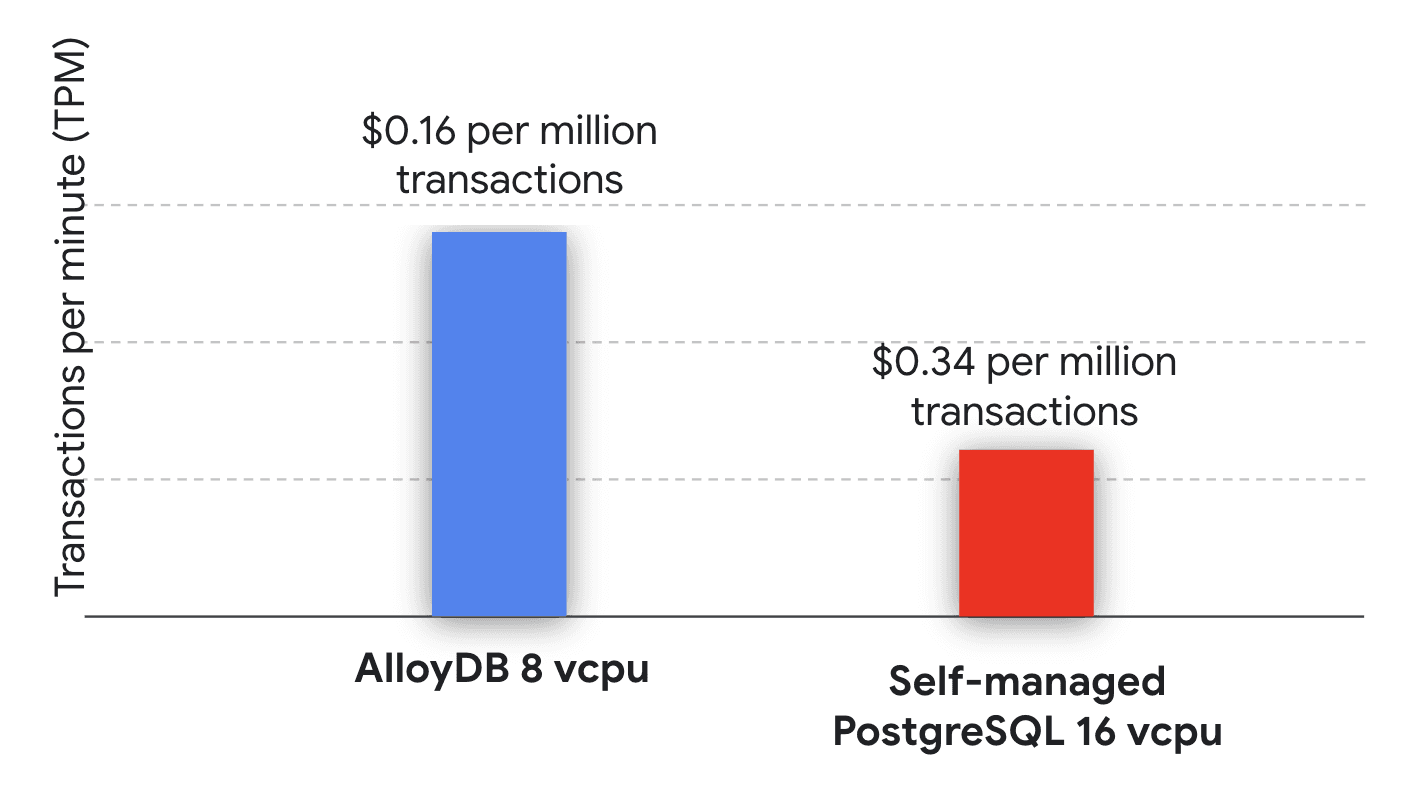
(Image source: GCP)
The most disruptive component of AlloyDB is the performance. Compared to the standard PostgreSQL service, AlloyDB is able to deliver more than 4x faster transactional workloads, with up to 2x better price-performance ratios.
Performance can be optimized by the intelligent caching layers, which accelerate the flushing of frequently queried data.
The rapid, responsive performance maintenance is due to the independent scaling of resource contention to the compute-storage.
Each cluster can support approximately 20 read pool instances.
Each individual cluster can be equipped with up to 128 virtual CPs and 864 GB of memory.
AI & ML Integration
Generative AI applications can be built on intelligent platforms due to AlloyDB AI, which enhances the capabilities of standard databases. The integration includes several specialized extensions:
Vector Database Capabilities: A customized pgvector extension can be used to connect SQL with semantic searches through innovative SQL and similarity searches.
High-Performance Search: The alloydb_scann extension leverages the Google Scanning ( ScaNN) algorithm to facilitate fast approximate searches.
ML Model Integration: Real-time text processing and embedding generation can be done through the use of AI tools, which are interconnected with Google’s ML model integration.
Natural Language Queries: The MS NLP module aids interaction with the database through the generation of SQL queries from English descriptions.
Reliability & Security
For every enterprise-grade reliability, AlloyDB runs on the backbone of Google Cloud, which offers a 99.99% uptime SLA, including maintenance windows.
Some of the security features offered are:
Automatic encryption: Data is encrypted at rest and in transit by default.
Customer-managed encryption keys: Full control over encryption keys.
IAM integration: Detailed access controls using Google Cloud IAM.
Network isolation: VPC integration for secure network configurations.
High availability configurations guarantee that automatic failover occurs in 60 seconds or less, with standby instances in distinct zones that ensure uninterrupted service during outages.
Hybrid Analytics Capabilities
For every AlloyDB hybrid query, transactional processes are integrated with analytical processing. AlloyDB performs up to 100x faster on analytical queries than standard PostgreSQL. With the columnar engine, transactional performance is not affected by the completion of complex analytical workloads.
This means there is no need for separate analytical databases or the complications involved in performing ETL processes. Directly against your transactional data, you can run business intelligence queries, reporting workloads, and real-time analytics.
AlloyDB Pricing Explained
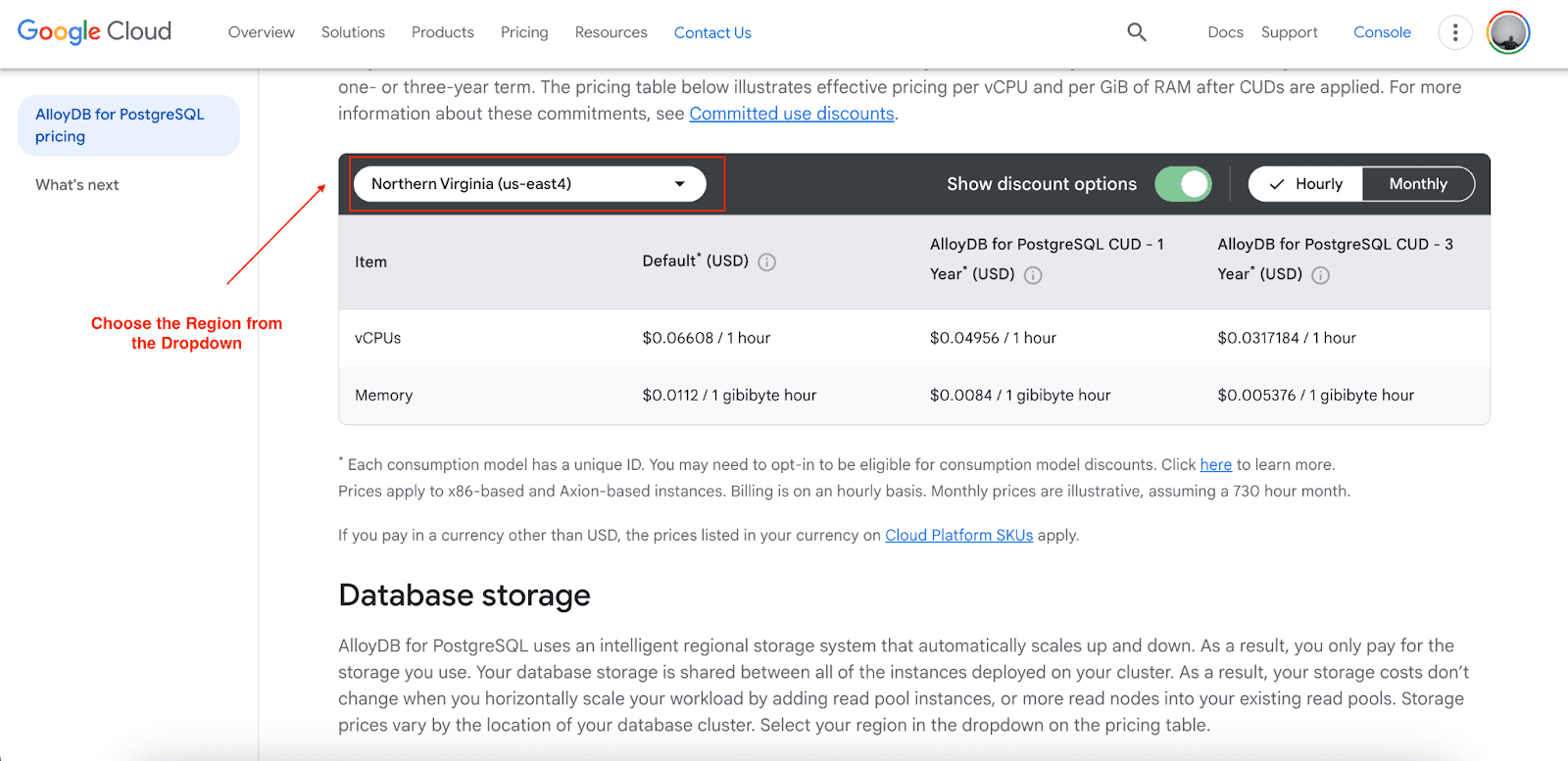
AlloyDB has a clear and simple resource-based pricing model, which allows one to accurately predict costs. The model has four core elements:
Compute Pricing (Northern Virginia - us-east4)
vCPUs: $0.06608 per hour (standard), with committed use discounts available
Memory: $0.0112 per gibibyte hour (standard)
Discounts are available for 1-year and 3-year commitments on compute costs.
Storage Costs
Database storage: $0.0004109 per gibibyte hour (approximately $0.30/GB/month)
Backup storage: $0.000137 per gibibyte hour (approximately $0.10/GB/month)
Automatic scaling: Pay only for storage you use, no pre-provisioning required
Networking Charges
Inbound data transfer: Free
Same-region data transfer: Free
Cross-region transfer: $0.02-$0.14 per GB, depending on the destination for cross-region transfer.
Outbound Internet egress: $0.12 per GB (0-1TB), with volume discounts available
Cost Comparison Example
For a typical enterprise workload requiring 16 vCPUs, 64 GB memory, and 500 GB storage:
AlloyDB Monthly Cost (Northern Virginia):
Compute: (16 × $0.06608 + 64 × $0.0112) × 720 hours = $1,275
Storage: 500 GB × $0.30 = $150
Total: $1,425/month
With a 3-year commitment and Pump optimization, this cost can drop by up to 52%.
While AlloyDB charges a 39% price premium over Cloud SQL Enterprise, performance and AI capabilities capitalize on additional costs for demanding workloads.
GCP AlloyDB vs Competitors
AlloyDB vs Cloud SQL
Choose AlloyDB when:
Performance needs to be better (4x faster transactions).
AI/ML integration is a requirement.
Analytical workloads run in parallel to transactions.
Enterprise-scale reliability is critical.
Choose Cloud SQL when:
PostgreSQL performance is standard.
Cost is the top issue.
Workloads are mostly transactional with no analytics.
AlloyDB vs Amazon Aurora
AlloyDB advantages:
Resource-based pricing is more affordable than request-based pricing.
PostgreSQL extensions are fully proprietary.
Some internally integrated AI capabilities do not need third-party services.
Data transfer to and from other regions is cheaper.
Aurora advantages:
More services are offered within the AWS ecosystem.
More developed serverless capabilities.
Better brand recognition.
AlloyDB vs Azure Cosmos DB
AlloyDB is not competing with the multi-model approach of Cosmos DB. Rather, AlloyDB focuses on high-performance PostgreSQL applications, and Cosmos DB addresses applications that need global distribution and various data models.
Getting Started with AlloyDB
Prerequisites Setup
Create or select a Google Cloud project with billing enabled
Enable required APIs:
AlloyDB API
Compute Engine API
Cloud Resource Manager API
Service Networking API
Cluster Creation Process
Create your first cluster:
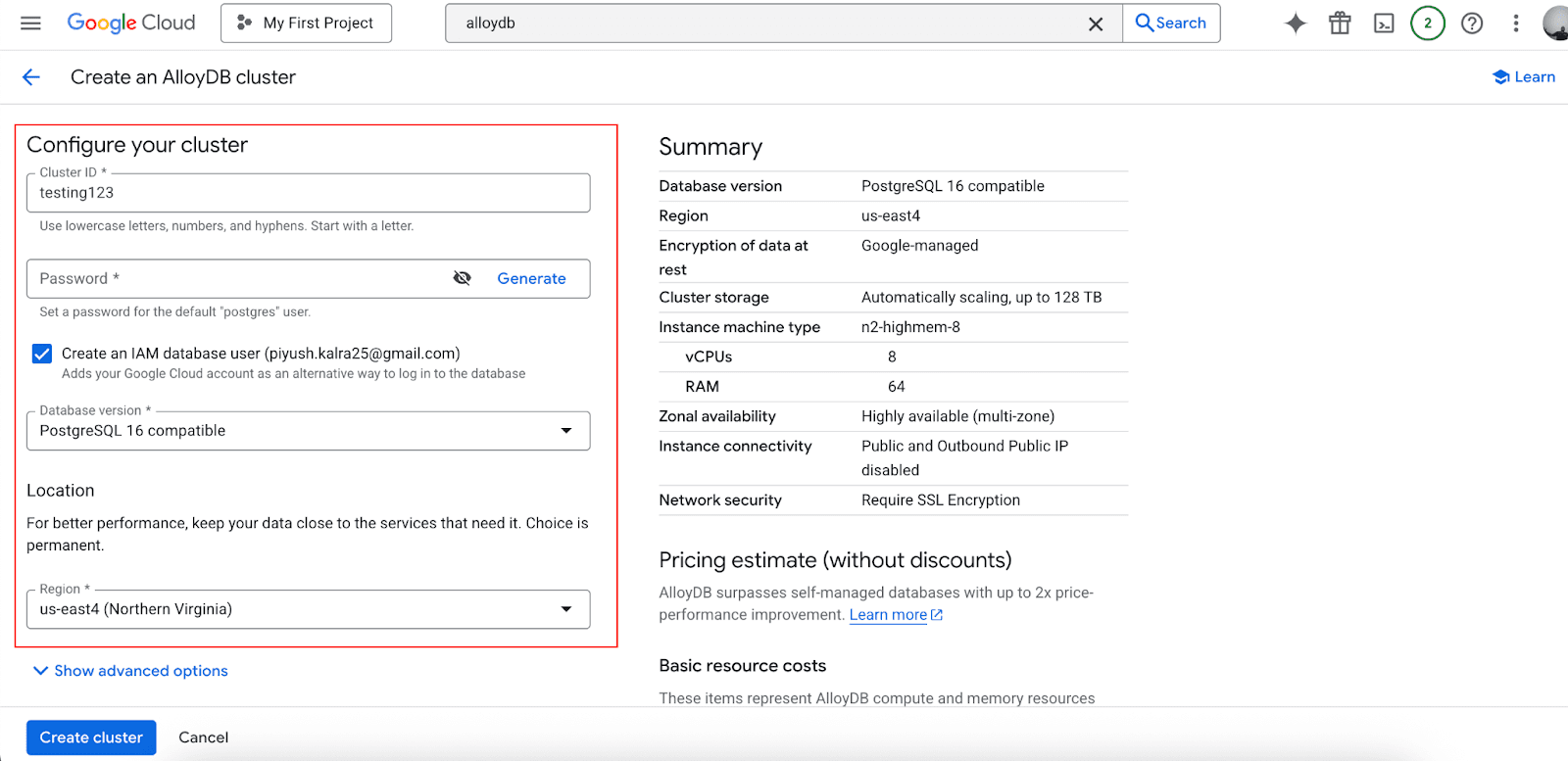
Choose region and availability configuration
Select machine types for the primary instance
Configure networking and security settings
Set backup and maintenance preferences
Connect your applications:
Use standard PostgreSQL connection strings
Configure SSL certificates for secure connections
Set up connection pooling for optimal performance
Pro tip: Start small, then scale resources as demand grows.
Who Should Use AlloyDB?
Startups: Want PostgreSQL and can scale effortlessly later.
Enterprises: Support hybrid workloads (transactions + analytics) smoothly.
Developers: Use tools with PostgreSQL and enjoy cloud-native speed.
Data Teams: Perform AI/ML workloads on transactional data in real time.
Maximize Your AlloyDB Savings with Pump
While AlloyDB offers excellent performance and capabilities, costs can accumulate quickly for growing businesses. These expenses can become a significant hurdle, especially for startups and scaling enterprises that need to manage their budgets carefully. This is where a cost optimization platform like Pump becomes invaluable. For example, a typical AlloyDB deployment costing $100 monthly could be reduced to just $48 with Pump's platform, delivering 52% savings automatically without any manual intervention.
Best of all, Pump is completely free to use
How Pump helps with GCP AlloyDB optimization:
AI-powered usage analysis and forecasting
Automated reserved instances discount purchases
Group buying benefits for volume discounts
Risk-free 30-day money-back guarantee
Conclusion
AlloyDB’s combination of PostgreSQL with AI for added functionality and performance, along with cloud-native application reliability, secures its standing as a frontrunner in database technology. Its clear pricing alongside its numerous functionalities simplifies the process of infrastructure modernization. Further savings are achieved with Pump’s cost optimization feature.
Google Cloud's free trial provides immediate access to AlloyDB, which enables real-time data processing and analytics. To improve operational efficiencies, Pump can be integrated to optimize costs.




