Consider yourself constructing a workflow that chains various AWS Services, such as a Lambda that prompts an S3 upload that then updates a DynamoDB table and probably sends a notification through an SNS. You probably realize how quickly these services can interconnect. What starts as an orderly workflow quickly becomes a tangle of retries, error management, sequencing, and monitoring that spans numerous services.
AWS Step Functions is built for this.
In this article, I will guide you through the various functionalities of AWS Step Functions, how they are utilized, as well as the practical application of the service if you are trying to create a flexible, scalable workflow within budget. You could be in the exploring phase of serverless computing, or heavily immersed in Lambda code. This guide is designed to aid you in understanding how to best utilize Step Functions for your serverless projects.
What Are AWS Step Functions?

AWS Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service. Think of it as a conductor for your cloud applications. It enables you to integrate a number of AWS services and construct a flexible workflow to make sure every service is well-orchestrated.
State machines are a collection of states, transitions, and associated actions, much like a flowchart. With each step as a “state” and Step Functions in charge of moving through the states. It deals with the issue, as well as the task retries, by automating the transitions. This strategy focuses on the primary business goals, while the automated workflow deals with the coordination of the distributed components.
How AWS Step Functions Work
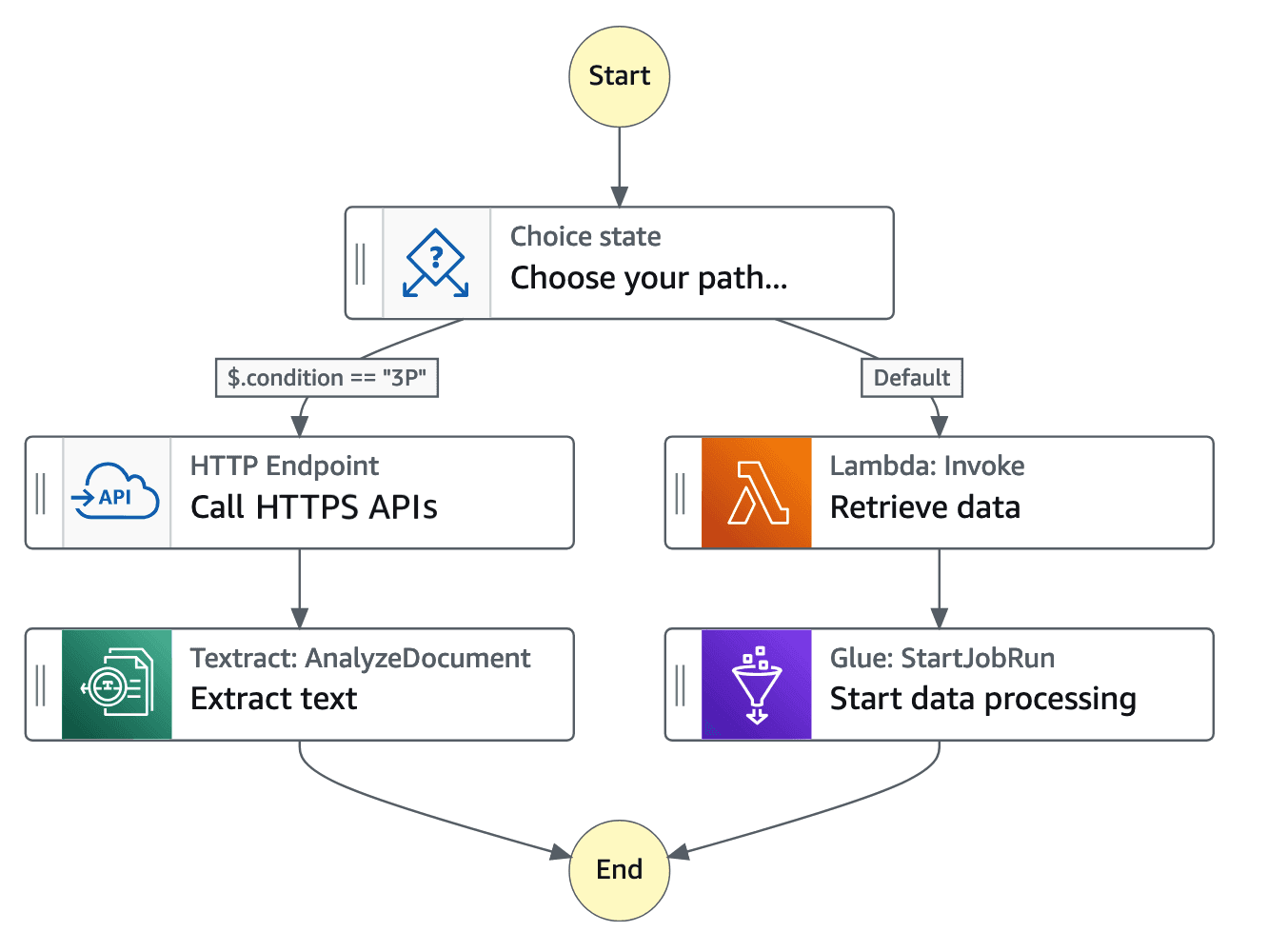
(Source: AWS)
So, how do you tell Step Functions what to do? You build a workflow on the Amazon States Language, a proprietary language that uses JSON syntax. If you find writing in JSON troublesome, AWS has a visual workflow builder where you can drag and drop components, and it will reverse-engineer the ASL code for you.
It may help to think about a workflow in terms of constituent steps, or “states,” which are narrowly defined, and each is assigned a distinct task:
Task State: This is the workhorse. It executes an atomic operation, such as invokes an AWS Lambda function, schedules a task on Amazon ECS, or issues a query to a database.
Choice State: The Choice state is configured to add if/then logic. Depending on the outcome of the earlier state, the Choice state determines the next sequence of steps to be executed: if a payment is captured, the box moves to the shipping step; else, an alert is raised.
Parallel State: This enables users to run multiple steps simultaneously in the workflow, which speeds the process.
Map State: This is for processing items in a list. Suppose you have 100 images to resize, and a Map state runs the same "resize" step concurrently for every image.
Wait State: This specifies that the workflow will be put on hold for a duration before performing the next action.
When executing workflows, Step Functions captures a comprehensive record for every action taken, weighing all the inputs and outputs. In a Step Function, every workflow completes with a model, making it easier to discover and rectify faults. These functions provide a log of every completion, eliminating the guesswork on where failures emerge.
Why Use AWS Step Functions?
So why use Step Functions instead of creating your own orchestration logic? The advantages are ease of use, reliability, and increased speed.
Simplified Orchestration
With Step Functions, you no longer have to write complex, and perhaps historically accurate, code and babysit cron jobs to weave together scheduled tasks for an application. Visual aspects that explain how the components of an application fit together are accessible to the designer. The service manages the state, and works the sequence for you.
Improved Reliability and Monitoring
Mistakes and failures will happen, and distributed systems will have them. Step Functions does have basic error handling, such as automatic retries. You can define Retry and Catch logic for each state to handle failures gracefully. The AWS Console allows for the execution to be traced visually to help quickly find and fix problems.
Scalability and Cost Efficiency
You do not have to maintain infrastructure for Step Functions; it is a serverless service. You can easily scale to cover your workload goals, no matter the execution of a day or the thousands you have to do in a second. You can also pay for only the Step Functions used, state transitions, or execution time.
AWS Step Functions Use Cases
The flexibility of Step Functions makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
Microservices Orchestration: Coordinate the communication between different microservices in an e-commerce platform, from order processing to inventory management.
Data Processing and ETL Pipelines: Automate complex data workflows, such as extracting data from a source, transforming it with AWS Glue, and loading it into a data warehouse.
IT and Security Automation: Create incident response workflows that automatically react to security alerts, like isolating a compromised EC2 instance.
Human-in-the-Loop Processes: Design workflows that require human approval, such as processing a loan application or moderating user-generated content.
Machine Learning Operations: Manage complete ML pipeline workflows, including data collection, model training, deployment, and regular scheduled retraining.
AWS Step Functions Pricing Explained
Prices depend on the workflow types you implement.
Standard vs. Express Workflows
Standard Workflows: These are best suited for processes that are long-running (up to one year), durable, and auditable. They are time-intensive, with an ‘exactly-once’ model of execution that prevents duplicates. You’re charged for each state transition. The free tier includes 4,000 free state transitions per month.
Express Workflows: These are useful in event processing workloads of high volume and short duration (up to 5 minutes). Examples are IoT data ingestion and streaming data processing. They operate on the ‘at-least-once’ model and are charged per execution and per time duration.
Pricing Example
Let’s go through a step-by-step breakdown of the pricing for a Standard workflow. After the free tier, the typical pricing per 1,000 state transitions is $0.025.
Assume your workflow has 10 states, and you operate it 100,000 times per month:
Total state transitions = 10 states * 100,000 executions = 1,000,000 transitions
Cost = (1,000,000 / 1,000) * $0.025 = $25 per month
Remember, this doesn't include the costs of the AWS services your workflow calls, such as Lambda or S3.
Best Practices for AWS Step Functions
To get the most out of Step Functions, follow these best practices.
Cost Optimization Tips
Reduce State Transitions: In a sequence of simple Lambda functions, try to condense and merge several functions to minimize transitions.
Choose the Right Workflow Type: Think of it like choosing the right tool for the job. Short and frequent jobs that need speed work best with Express Workflows. Standard Workflows work best for long, critical jobs that need reliability and auditing. Combining both will sometimes save you more.
Avoid Large Payloads: State payloads are limited to 256KB. For anything larger, you will need to save the data to an S3 bucket and, between the states, pass the objects and resource name (ARN).
Monitor Costs: Use AWS Cost Explorer and CloudWatch to help monitor transition costs, execution times, and resource-intensive workflows.
Set Timeouts: Avoid tasks running forever. Timeouts should be set to save you from great costs and inefficient operations due to excessive resources spent on tasks that hang.
Limit Retries: Use limits on the number of times a process can be tried in a set period of time, and a delay should be used to incrementally increase the time between attempts. This prevents "runaway loops," which, in the context of a task, can be compared to an unrestricted pass for an expiration check.
Workflow Design Best Practices
Use Clear State Naming: “ValidateOrder” is preferable to “Lambda1.” Give your states descriptive names to make your workflow easier to understand and debug.
Start New Executions for Long Loops: Create new executions to help with the continuation of the workflow instead of creating large loops in a single run and risking the 25,000 history limit.
Is AWS Step Functions Right for You?
Definitely yes, if you are using AWS to coordinate various services, Step Functions can be a great asset. It simplifies the orchestration of workflows, error handling, and provides visibility for every process step.
However, like any powerful tool, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. For simple, single-service use cases or event-driven AWS Lambda functions, it can be overly complex. It is similar to using a fully fledged orchestra for a simple solo performance. It simply would be too much.
Once your workflows integrate various services, complexity, dependencies, retries, or even require approval steps, Step Functions really come into their own. It transforms your process from a convoluted mess to a smooth, orderly, and reliable symphony.
Conclusion
AWS Step Functions is one of those services you don’t appreciate until you need it, kind of like a good plunger. It’s elegant, visual, and deeply integrated with the AWS ecosystem. More importantly, it helps you build reliable workflows that scale gracefully without reinventing the orchestration logic.
Hopefully, this article helped you understand what AWS Step Functions is all about. If you’re ready to bring order to your AWS chaos, Step Functions is your new best friend.
Join Pump for Free
If you are an early-stage startup that wants to save on cloud costs, use this opportunity. If you are a start-up business owner who wants to cut down the cost of using the cloud, then this is your chance. Pump helps you save up to 60% in cloud costs, and the best thing about it is that it is absolutely free!
Pump provides personalized solutions that allow you to effectively manage and optimize your Azure, GCP, and AWS spending. Take complete control over your cloud expenses and ensure that you get the most from what you have invested. Who would pay more when we can save better?
Are you ready to take control of your cloud expenses?




