When you are busy running projects, processing big data can become overwhelming as it has too much data to compute. IT systems often collapse and can become clustered. One good solution is managed big data platforms such as AWS Elastic MapReduce. This will allow for efficient processing, data management, and analysis when it comes to AWS EMR. This is great for companies, as it allows for efficient management of data when it comes to large-scale data warehousing, complex ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), and machine learning, as it helps automate several processes in data analysis.
AWS EMR enables users to run the most popular open-source big data frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark without the headache of configuring complex clusters for weeks. Instead, users can configure and have a complex, scalable environment operational in a matter of minutes.
In this article, I will walk you through what AWS EMR is, its key features, how its pricing works, and how to optimize your costs.
What is AWS EMR?

AWS EMR refers to Elastic MapReduce, which is a big data platform delivered in the AWS cloud, AND that facilitates the use of certain distributed data processing frameworks. AWS EMR is a managed service focused on the complex tasks of setting up, configuring, and scaling big data environments.
Traditionally, running a Hadoop or Spark cluster was tied to the costly acquisition of hardware resources and the investment of numerous configuration and maintenance hours. The service provided by AWS EMR Django is able to take care of provisioning a cluster of your choice. It will set up a number of Amazon EC2 instances and will install all the required software components. Having this functionality would enable the data teams to focus on the extraction of important and valuable data.
Use of AWS EMR is relevant for:
Data Mining & Analysis: Allows for the discovery of various patterns and trends in a subset of larger databases.
Machine Learning: Preparing and separating data in bulk to be used for training predictive systems.
Log Analysis: Processing and analyzing application logs for operational insights and monitoring.
ETL Workflows: Transforming and moving large datasets between different data stores.
How AWS EMR Works
The fundamental structure of an EMR cluster is a configuration of roles of individual EC2 instances. This structure is optimized for workload splitting for parallel processing of data and tasks:
Primary Node: This is the head of the cluster and the one responsible for overseeing the orchestration. The node is in charge of the infrastructure and keeps track of the data and the tasks, as well as over all health of the cluster
Core Nodes: These are the nodes that execute the commands and processes given by the primary node. These nodes are responsible for the data processing and storage in the HDFS, which runs adjacent to the nodes.
Task Nodes: As an optional integration, nodes that have the capacity to run additional processes are deemed task nodes. These nodes, unlike the others, are non-HDFS data storage nodes and thus are well-suited for processing heavy workloads.
The initial step is the ingestion of data, for example, from S3 storage. The data is subsequently processed by an EMR cluster comprising Hadoop or Spark, and the results are returned to AWS S3 storage or other services like AWS Redshift.
AWS EMR works closely with other key AWS services. For example, Amazon S3 provides low-cost, durable storage, while Amazon CloudWatch provides monitoring and log storage for the EMR cluster. Such integration enables a cohesive and robust framework for big data analytics on AWS.
Key Features of AWS EMR
AWS EMR offers a set of features for flexible, scalable, and secure big data processing:
Scalability: EMR clusters scale up or down based on the workload demands. This auto-scaling ability makes certain that resources aren’t paid for when they are dormant.
Flexibility: EMR platforms are compatible with a wide range of open-source tools, including Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Presto, Hive, and HBase.
Integration: EMR allows storage and retrieval of data from Amazon S3, the use of AWS Glue Data Catalog as a metadata store, and direct data querying using Amazon Athena.
Cost-Efficiency: Amazon EMR offers economical processing. Users pay per second of usage on streaming instances, and EMR can use Amazon EC2 Spot Instances to reduce compute expenses for fault-tolerant workloads by up to 90%.
Security: EMR offers strong security capabilities, such as coupling with AWS IAM to grant specific access, strong encryption of data at rest and during transit, and strong protections for clusters launched within a VPC.
AWS EMR Pricing Explained
Pricing for AWS EMR is influenced by many aspects, such as the time spent on it, the installation strategy for the EMR apps, and the kind of installation selected. Here's a detailed breakdown of how AWS EMR pricing works:
How Pricing for Amazon EMR on EC2 Works
With Amazon EMR on EC2, you get billed based on the duration of time spent on it, and a minimum of 60 seconds is required. Normally, you get billed by the hour. Payments for the deployment model also matter. You can deploy Amazon EMR with EC2 instances or with AWS Fargate. In all of these cases, you pay for the EC2 or Fargate resources in addition to the EMR hourly rate.
On the subject of deployment types, there are four types that Amazon EMR supports, and they all have different pricing:
1. Pricing for Amazon EMR on EC2 Instances
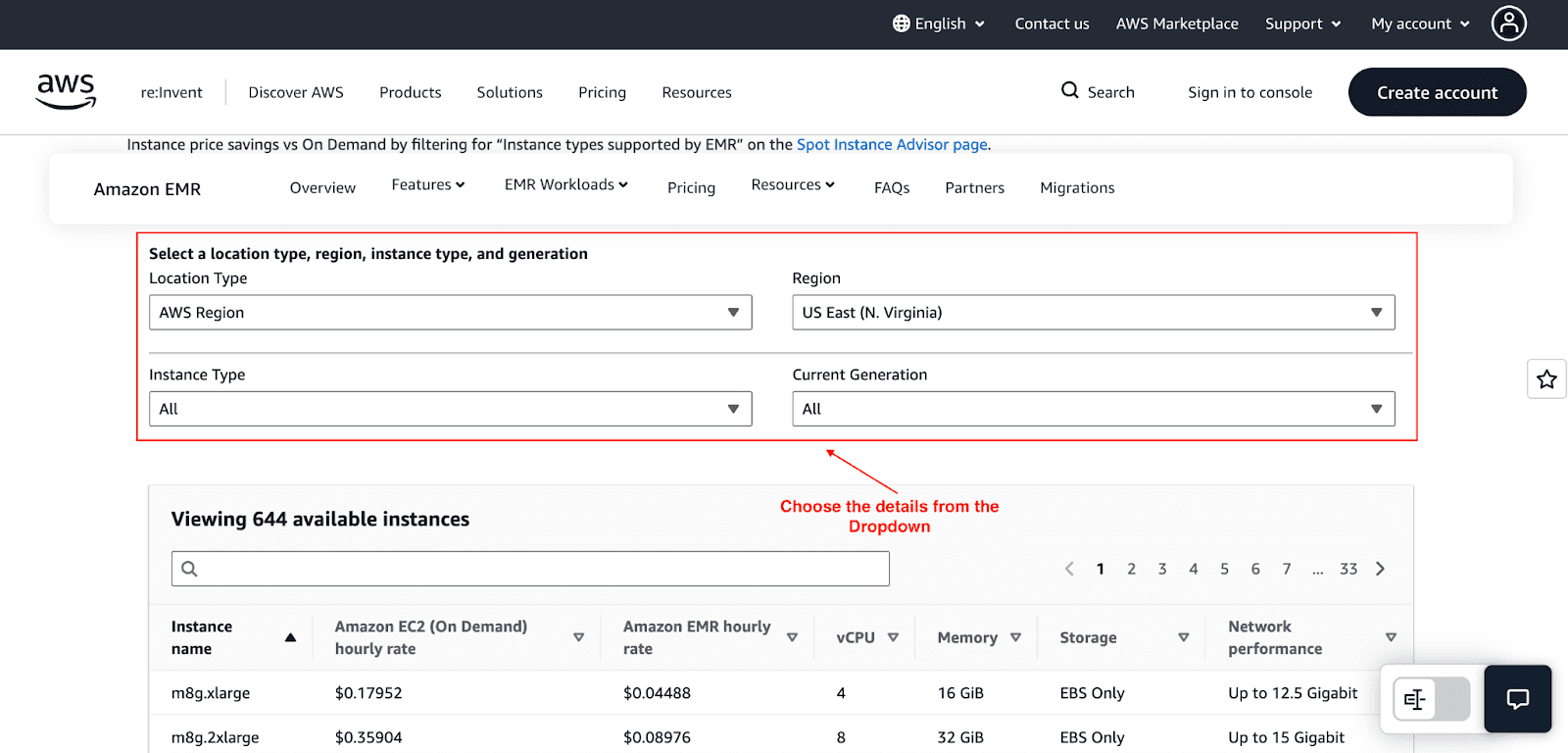
Pricing is based on the AWS Region, instance type, the length of time in use, and the purchase model, which could be On-Demand, Reserved Instances, or Spot Instances. For example, running Amazon EMR on an m8g.8xlarge EC2 instance in the US East (N. Virginia) Region will incur a cost of $1.43616 for an hour on the EC2 instance, and $0.35904 for an hour on the EMR service.
2. Pricing for Amazon EMR on EKS Clusters
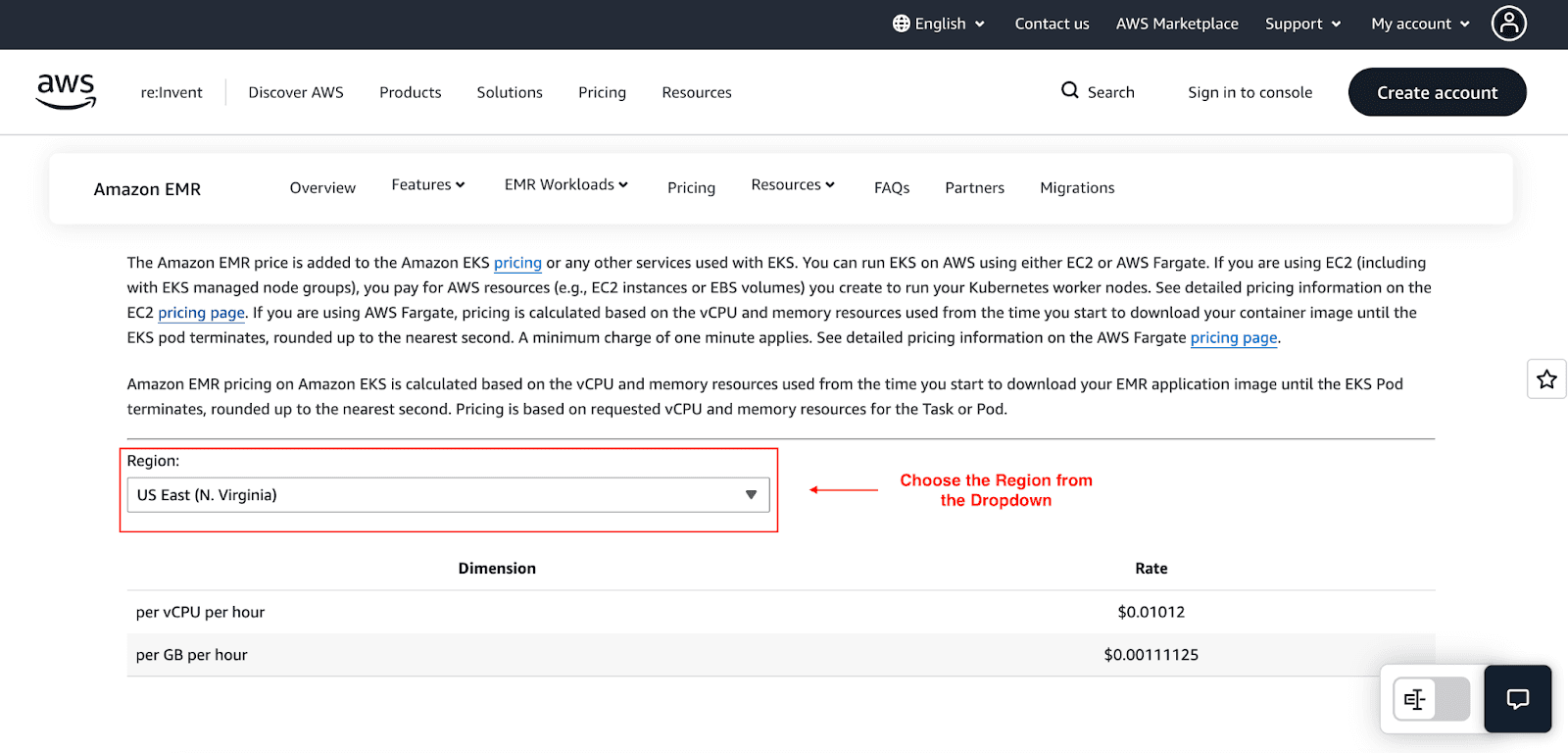
With Amazon EMR on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service, you pay for memory and vCPUs processing by your tasks or pods. The billing captures the period from the commencement of image downloads and ceases when engagement of the task or pod is done. There's a minimum of a 60-second billing window. For example, in the US East (N.Virginia) Region is priced at $0.01012 per vCPU per hour and $0.00111125 per GB per hour of memory.
3. Pricing for Amazon EMR on AWS Outposts
Running Amazon EMR on AWS Outposts, the pricing structure is like that of EMR on the cloud. Nevertheless, the pricing will vary depending on the particular arrangement of your Outposts hardware and the requirements for your deployment.
4. Pricing for Amazon EMR Serverless
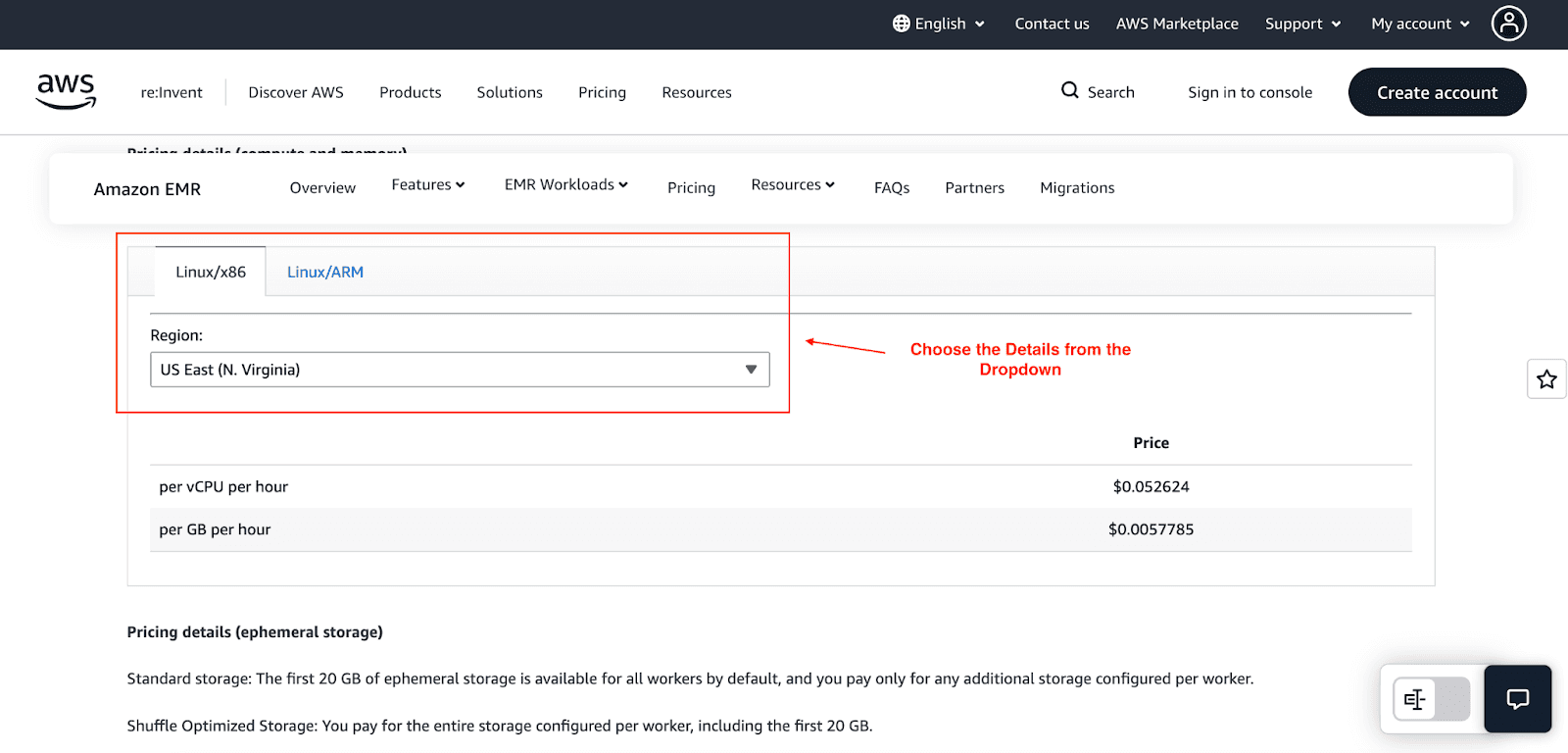
With Amazon EMR Serverless, charges will apply for all the vCPUs and memory used, which are termed as compute resources, along with the storage used collectively by your applications on all the worker nodes. For example, in the US East (N.Virginia) Region, the compute charges are $0.052624 for every vCPU per hour, and $0.0057785 per GB of memory used per hour. Also, any additional ephemeral storage above the 20 GB free allowance is charged $0.000111 per GB per hour.
For specific and up-to-date pricing for AWS services and tools, including Amazon EMR, you are advised to check the AWS pricing pages, which monitor changes.
Factors That Affect EMR Pricing
Several factors can influence your final bill:
Instance types and count: Larger and more powerful instances cost more.
Duration of cluster usage: The longer your cluster runs, the more you pay.
Data transfer and storage: Moving data in and out of EMR and storing it in S3 incurs costs.
Data locality: Keeping your data in the same region as your EMR cluster helps avoid data transfer charges.
Comparing AWS EMR with Alternatives
Feature | AWS EMR | Google Dataproc | Azure HDInsight |
Pricing | Per instance-hour | Per vCPU-hour | Per node-hour |
Scaling | Auto-scaling | Auto-scaling | Manual or auto |
Framework Support | Hadoop, Spark, Presto, Hive, HBase | Hadoop, Spark, Hive | Hadoop, Spark |
Integration | Deep with AWS | Deep with GCP | Deep with Azure |
Cost Control | Spot, RIs, Savings Plans | Preemptible VMs | Reserved VMs |
In my opinion, AWS EMR generally wins on integration, pricing, and flexibility.
Cut AWS EMR Costs with Pump
Running big data jobs on AWS EMR can become expensive, particularly when clusters are left running idle or are configured with overpriced On-Demand EC2 instances. Without changing your workflows, Pump helps you reduce your costs.
Here is how we help you save costs:
Instant EC2 Discounts: Since EMR runs on EC2, most of your cost comes from these instances. We use group buying power from thousands of startups to give you access to enterprise-level EC2 discounts, allowing you to pay less per hour for the same EMR clusters.
Automated Cost Monitoring: We use AI to automatically monitor your AWS costs and highlight inefficiencies, so you can quickly detect and fix idle or oversized clusters before they waste budget.
Smart Instance Mix: Pump’s AI engine continuously analyzes your AWS billing patterns to recommend the most cost-effective mix of Savings Plans and Reserved Instances. It ensures you maximize AWS resource savings without compromising availability, all without manual intervention.
Best of all, Pump is entirely free. No hidden costs, no subscriptions, just cost optimization while you enjoy your coffee.
Best Practices for Optimize EMR Costs
To fully realize your savings, implement the following practices:
Auto-Terminate Idle Clusters: To avoid exposure to costs associated with idle resources, configure clusters to auto-terminate after the completion of a job.
Use Instance Fleets: Increase availability while decreasing costs by diversifying your instance types and utilizing several Spot pools.
Tag Your Clusters: Apply a consistent tagging strategy to accurately distribute EMR costs by team, initiative, and organization.
Use Graviton Instances: Select Graviton instances at lower price points, which are ARM-based and still deliver equivalent performance for your workloads.
Monitor with CloudWatch: Avoid overprovisioning by tracking CloudWatch data on memory and CPU utilization.
Store Data in S3: Store data in Amazon S3 for long-term retention for the purpose of separating compute from storage and paying for what you actually use.
Conclusion
AWS EMR is an indispensable tool for organizations looking to harness the power of big data. It offers a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective platform for a wide range of data processing tasks. We trust that by exploring its features, architecture, pricing, and these proven optimization strategies, you have gained a comprehensive understanding of how to use EMR efficiently and cost-effectively.
Ready to take your cost optimization to the next level? Start optimizing your EMR costs with Pump’s automated insights and cloud discounts.




